Xiangdafeng Technology (Beijing) Co., Ltd Copyright No.2020041289-1
Address:712, 7th floor, building 154, brick factory Beili, Tongzhou District, Beijing
Mobile:+86 18901353186 Tel:010-82900580
Fax:010-82900580Mail:market@xdfpcba.com

What is the through hole design?
Vias are one of the important parts of Multilayer PCB. The cost of drilling usually accounts for 30 to 40% of PCB board making cost. From the PCB design point of view, a hole is mainly composed of two parts: one is the drill hole in the middle, the other is the welding pad area around the borehole. The size of these two parts determines the size of the hole. Obviously, in the design of high-speed and high density PCB, designers always hope that the smaller the vias, the better, so that more wiring space can be reserved on the board. In addition, the smaller the vias, the smaller their parasitic capacitance is, and is more suitable for high-speed circuits.
However, the decrease of hole size brings about the increase of cost, and the size of the hole can not be reduced without limitation. It is limited by the drilling and plating technology. The smaller the hole, the longer the drilling time is, the more likely it is to deviate from the center position; and when the depth of the hole exceeds 6 times the diameter of the hole, the uniform copper plating on the hole wall cannot be guaranteed.
PCB design specification for hole passing
In principle, the inner diameter of the full passing hole shall be 0.2mm (8mil) and above, and the outer diameter shall be above 0.4mm (16mil), and the outer diameter shall be controlled at 0.35mm (14mil) in case of any difficulty;
Tip small assistant: according to the size of the diameter and outer diameter of the commonly used hole size of PCB, the X * 2 ± 2mil (x is the inner diameter). For example, the hole with the diameter of 8mil can be designed as 8/14mil, 8/16mil or 8/18mil; for example, the hole of 12mil can be designed as 12/22mil, 12/24mil and 12/26mil;
2. BGA design proposal of 0.65mm and above is not to use blind hole, and the cost will increase greatly. When the blind hole is used, the first-order blind hole is generally used (top layer-l2 layer or bottom negative L2), the inner diameter of the passing hole is generally 0.1mm (4mil), and the outer diameter is 0.25mm (10mil), as shown in Figure 1-1.
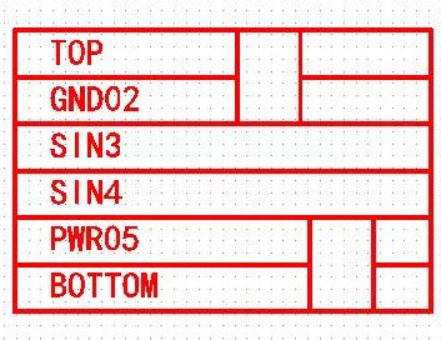
Figure 1-1 schematic diagram of first order blind hole
3. Vias should not be placed on pads smaller than the size of 0402 resistor capacitance pads. Theoretically, the lead inductance is small when placed on pads, but the solder paste is easy to enter vias during production, resulting in uneven solder paste and device standing up ("monument phenomenon"). Generally, the recommended spacing is 4-8mil, as shown in Figure 1-2.
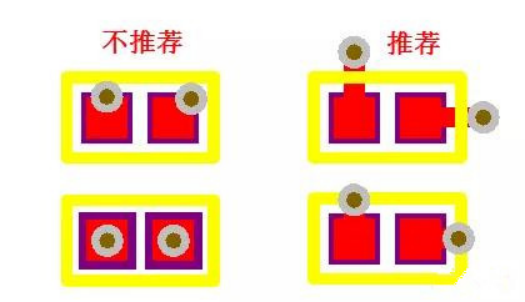
Figure 1-2 schematic diagram of via to pad drilling
4. The spacing between through holes should not be too close. Drilling is easy to cause hole breakage. Generally, the hole spacing is required to be 0.5mm or more, 0.35mm-0.4mm should be avoided, and 0.3mm or less is prohibited, as shown in Figure 1-3;
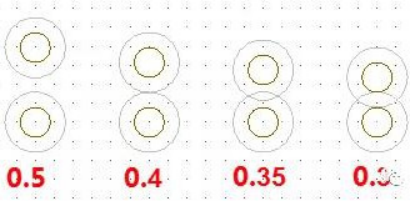
Figure 1-3 spacing between vias
5. As shown in Figure 1-4, in addition to the heat dissipation through hole, the through hole ≤ 0.5mm needs to be plugged and covered with oil (the inner diameter is 0.4mm, the hole needs to be plugged).
1) Especially for the devices with metal shell, no through hole shall be drilled under the body in principle, and certain plug holes with through hole shall be covered with oil to avoid short circuit between shell and through hole.
2) According to the feedback from the plate manufacturer, it is often mentioned that the BGA via is too close to the pad and needs to be moved. This situation is caused by that the vias are not equidistant from the BGA pads. At present, it is normal that the vias and test holes under bag are not equidistant from the BGA pads. PCB designers do not pay attention to this, which leads to continuous engineering problems and also a hidden danger to the welding quality. Therefore, we directly recommend drilling to the center of the two pads. Especially in BGA, due to the small pitch distance, the through hole plug hole under BGA needs to be covered with oil after drilling, so as to avoid short circuit of BGA ball.
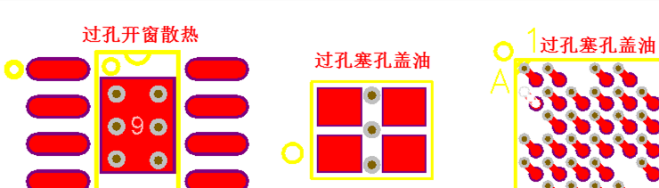
Figure 1-4 through hole application scenario
6. The fixed welding pad such as earphone terminal, key, FPC, etc. is to prevent the copper skin from falling off. If the conditions permit, 1-2 vias (evenly placed through holes) are drilled on the welding pad, which can effectively improve the "fixity", as shown in Figure 1-5.
Figure 1-5 placement of fixed pad through hole
7. Fan hole
In PCB design, the fan out of vias is very important. The fan out mode will affect the signal integrity, plane integrity, the difficulty of wiring, and even the cost of production.
1) As shown in Figure 1-6, the recommended method for fan hole and defect of conventional chip devices can cross the line between the two holes in the inner layer, and the reference plane will not be split. On the contrary, the not recommended method increases the difficulty of wiring, and also splits the reference plane, damaging the plane integrity.
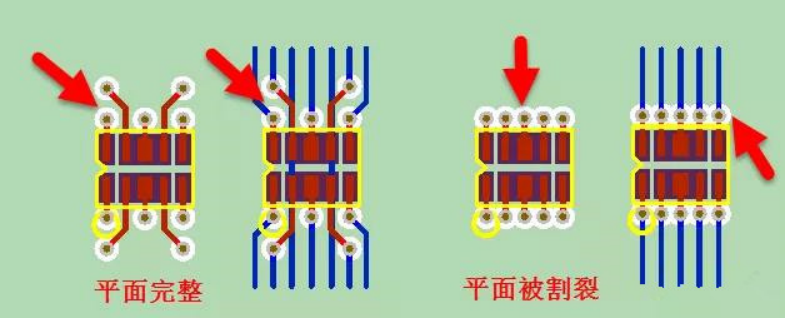
Figure 1-6 comparison of fan out modes of conventional chip devices
Similarly, this kind of device fanning method is suitable for the situation of drilling and layer replacement, as shown in Figure 1-7.
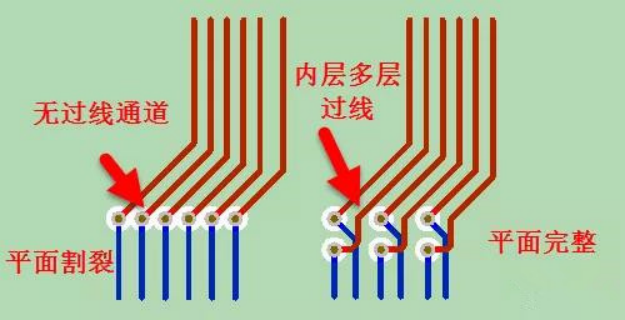
Figure 1-7 application scenario of drilling and layer replacement
2) BGA fan hole mode
BGA fan holes should not be punched on the pad. It is recommended to punch in the middle of the two pads. Many engineers move the position of the via in BGA at will for the convenience of outgoing line, and even punch it on the pad, as shown in Figure 1-8, resulting in irregular via in BGA area, which is easy to cause the problem of false welding in later welding, and may damage the plane integrity.
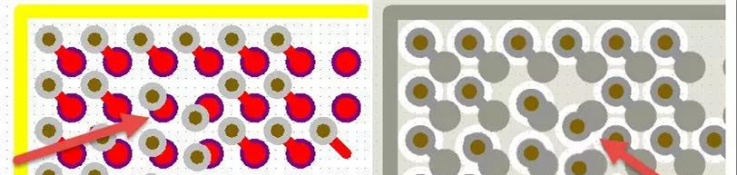
Figure 1-8 example of hole in BGA disc
Three key processes in HDI PCB......
Why plug holes should be made ......
Analysis of the main causes of......
PCB design company analyzes th......
PCB via design specification...
The type selection of componen......
Common PCB high frequency and ......
Factors affecting PCB cost...
SMT customer incoming material......
Definition and classification ......
Consultation hotline
010-82900580